Coolant Temperature Sensor Resistance Values: Ultimate Guide
Understanding coolant temperature sensor resistance values is crucial for car maintenance. These values help diagnose engine problems.
Coolant temperature sensors monitor engine temperature. They send data to the car’s computer. This information ensures optimal engine performance. Knowing the correct resistance values can save you from costly repairs. It helps in detecting issues early. In this blog, we’ll explore the significance of these values.
You’ll learn how they work and why they’re essential. This knowledge is vital for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics. Let’s dive into the world of coolant temperature sensors and their resistance values.
Introduction To Coolant Temperature Sensors
Coolant temperature sensors are key in engine performance. They measure the temperature of the engine’s coolant. This data helps the engine control unit (ECU) adjust the fuel injection.
The sensor ensures the engine runs at its best temperature. This prevents overheating and improves fuel efficiency. Using a faulty sensor can lead to poor engine performance and higher fuel consumption.
The sensor sends data to the ECU. The ECU uses this data to manage the air-fuel mixture. This is vital for smooth engine operation. It also helps in reducing emissions.
A working sensor ensures the engine stays within a safe temperature range. This protects the engine parts from damage. Regular checks can help identify issues early.
How Coolant Temperature Sensors Work
Coolant temperature sensors measure the temperature of the engine’s coolant. These sensors are vital for engine performance. They help the engine control the fuel mixture. Sensors use resistance to measure heat. Hot coolant makes resistance drop. Cold coolant makes resistance rise. This change tells the engine computer how hot the engine is. The computer adjusts the fuel and air mix. This keeps the engine running smoothly.
Coolant temperature sensors are usually near the thermostat. They can also be in the cylinder head. This location helps measure the coolant temperature accurately. Sensors must be placed where coolant flows. This ensures correct readings. Correct readings help the engine run better. Wrong placement can cause engine problems. Always check your car manual for the exact sensor location.
Types Of Coolant Temperature Sensors
NTC stands for Negative Temperature Coefficient. This means the resistance decreases as the temperature increases. NTC sensors are common in cars. They help measure engine temperature. They are easy to use and cost-effective. NTC sensors can measure a wide range of temperatures. They are reliable and accurate. Many car companies use them.
PTC stands for Positive Temperature Coefficient. This means the resistance increases as the temperature increases. PTC sensors are also used in cars. They are not as common as NTC sensors. PTC sensors are used in safety devices. They help protect engines from overheating. PTC sensors are more expensive. They are also more sensitive to changes in temperature.

Credit: www.pinterest.com
Reading Resistance Values
You need a digital multimeter. A pair of gloves is also useful. Ensure you have a clean cloth. A flashlight can help too.
First, locate the coolant temperature sensor. It is near the engine block. Use the flashlight if needed. Put on your gloves.
Next, disconnect the sensor from its wiring harness. Now, set your multimeter to the resistance setting. Place the probes on the sensor terminals.
Observe the resistance value on the multimeter. Compare this with the manufacturer’s specifications. Ensure it falls within the expected range.
Interpreting Resistance Values
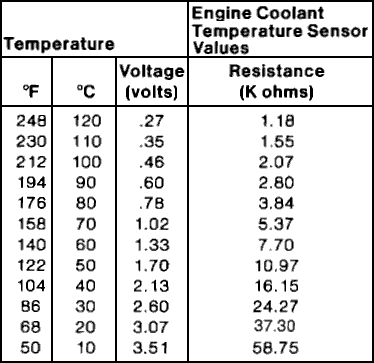
The coolant temperature sensor has standard resistance values. These values vary with temperature. For example, at 0°C, the resistance might be 5,000 ohms. At 20°C, it might be 2,500 ohms. At 80°C, the resistance could be around 300 ohms. Always check the vehicle manual for exact values.
Sometimes, the sensor shows different values. A faulty sensor may give a high resistance. This can cause the engine to run cold. A low resistance can cause the engine to overheat. Regular checks help avoid these issues. Replace the sensor if values are off by much.
Credit: www.stevesnovasite.com
Troubleshooting Sensor Issues
A car might overheat. The engine may misfire. Fuel consumption could increase. The dashboard warning light might turn on. The car might idle roughly. Poor acceleration is another sign. The cooling fan could run constantly. These issues point to a bad sensor.
Use a multimeter to check the sensor. Ensure the engine is cold. Disconnect the sensor. Measure the resistance across its terminals. Compare values with the manual. If values differ, the sensor is faulty. Replace the sensor if needed. Regular checks prevent larger issues.
Replacing The Coolant Temperature Sensor
The engine’s temperature gauge may stop working. This can be a sign. Overheating issues might also arise. Your car may consume more fuel. The engine might run poorly. These are all signs. Time to replace the coolant temperature sensor.
First, turn off the engine. Let it cool down. Locate the coolant temperature sensor. It is usually near the thermostat. Disconnect the battery. This ensures safety. Use a wrench to remove the old sensor. Install the new sensor. Tighten it firmly. Reconnect the battery. Start the engine. Check for leaks. Ensure the temperature gauge works well.
Credit: www.explorerforum.com
Maintenance Tips
Check the coolant temperature sensor every six months. This helps catch issues early. Clean the sensor with a dry cloth. Avoid using water or chemicals. Inspect for any visible damage. Replace the sensor if needed. This keeps your vehicle running well.
Use the right coolant for your car. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines. Avoid mixing different types of coolant. This prevents sensor damage. Keep the coolant level within the recommended range. Low coolant can cause overheating. Regularly check for leaks in the cooling system. Fix any leaks immediately. This protects the sensor and engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Normal Resistance Of A Temperature Sensor?
The normal resistance of a temperature sensor varies, typically ranging from 100 ohms to 1000 ohms. Standard RTDs often have 100 ohms at 0°C. Thermistors can vary widely, commonly at 10,000 ohms at 25°C. Always check the sensor’s datasheet for exact specifications.
How Many Ohms Should A Coolant Level Sensor Have?
A coolant level sensor typically measures between 1,000 to 4,000 ohms. Exact values depend on the specific vehicle and sensor type.
How Do You Test A Coolant Temperature Sensor With A Multimeter?
Set the multimeter to the resistance setting. Disconnect the sensor’s electrical connector. Measure the sensor’s resistance across its terminals. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
How Do You Know Your Coolant Temperature Sensor Is Bad?
Check for engine overheating, poor fuel economy, or the engine light on. An erratic temperature gauge indicates a faulty sensor.
Conclusion
Understanding coolant temperature sensor resistance values is crucial for car maintenance. These values help monitor engine temperature. Regular checks prevent overheating issues. Simple tools can measure these values accurately. Correct readings ensure optimal engine performance. Always consult your vehicle’s manual for specific values.
Proper maintenance extends your car’s lifespan. Stay informed and keep your engine running smoothly. Regular sensor checks are a small but vital task. Ensure your car’s health with accurate sensor readings. Happy driving and safe journeys!




