5.9 Cummins Coolant Flow Diagram
The 5.9 Cummins coolant flow diagram is a crucial component in maintaining optimal engine performance. Understanding the flow path through the engine and its components, including the radiator, water pump, thermostat, coolant lines, expansion tank, and heater core, is essential for diagnosing and resolving flow issues.
Regular maintenance and upkeep of the coolant system are also critical for ensuring optimal performance. By mastering the 5.9 Cummins coolant flow, you can optimize your engine’s performance and avoid costly repairs.
The coolant flow diagram is a vital component in the 5.9 Cummins engine, as it allows for proper circulation of coolant to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance.
Understanding the coolant flow diagram and the main components of the coolant system is essential for maintaining the engine’s health and performance.
Related Article: Chevy 350 Coolant Flow Diagram
In this guide, we’ll provide an overview of the 5.9 Cummins coolant flow diagram and the key components involved.
Cummins- How to the coolant flow in the engine.
6 Components of the Coolant System
As I mentioned earlier, the coolant system is a critical component of the 5.9 Cummins engine. It helps to regulate the engine’s temperature and prevent overheating, which can cause significant damage to the engine if left unchecked. Here’s a closer look at the main components of the coolant system:
1. Radiator
The radiator is responsible for cooling the engine coolant as it flows through the system. It’s a large, metal component with a series of thin, flat tubes that allow the coolant to flow through them.
As the coolant passes through the tubes, the heat is dissipated, and the coolant is cooled before being recirculated through the engine.
2. Water Pump
The water pump is responsible for circulating the coolant through the engine and the radiator. It’s usually located on the front of the engine and is driven by a belt connected to the crankshaft.
As the engine runs, the water pump circulates the coolant through the system, keeping the engine at a safe operating temperature.
3. Thermostat
The thermostat is a small, valve-like component that regulates the flow of coolant through the engine. It’s usually located at the engine’s front and is designed to open and close as needed to regulate the engine’s temperature.
When the engine is cold, the thermostat is closed, which allows the engine to warm up more quickly. When the engine reaches its operating temperature, the thermostat opens, allowing the coolant to circulate freely.
4. Coolant Lines
The coolant lines are a series of hoses and pipes that transport the coolant through the system. They connect the radiator to the engine, the water pump to the thermostat, and the heater core to the engine, among other connections.
The coolant lines are usually made of rubber or metal and are designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the engine.
5. Expansion Tank
The expansion tank, also known as the overflow tank or coolant reservoir, is responsible for storing excess coolant as the engine heats up and the coolant expands. It’s usually located near the radiator and is designed to prevent coolant from overflowing out of the system.
The expansion tank also serves as a visual indicator of the coolant level, allowing you to monitor the system’s health and prevent potential problems.
6. Heater Core
The heater core is a small radiator-like component that’s responsible for heating the cabin of the vehicle. It’s usually located behind the dashboard and is connected to the engine’s coolant system.
As the engine circulates the coolant through the system, some of the heated coolants flows through the heater core, which heats the air that’s blown into the cabin by the vehicle’s HVAC system.
Note, understanding the components of the coolant system in the 5.9 Cummins engine is crucial for maintaining its health and performance. By regularly checking and maintaining these components, you can prevent overheating and other potential problems that could lead to costly repairs.
Coolant Flow in the 5.9 Cummins Engine
The coolant flow in the 5.9 Cummins engine begins with the water pump, which pulls the coolant from the radiator and circulates it through the engine. The coolant then flows through the engine block and cylinder head, where it absorbs the heat generated by the combustion process.
From there, the heated coolant flows through the thermostat, which regulates the flow based on the engine’s temperature. If the engine is too cold, the thermostat remains closed, allowing the coolant to circulate only through the engine block and cylinder head until the engine warms up.
Once the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature, the thermostat opens, allowing the coolant to flow through the radiator and cool down before recirculating through the engine.
As the coolant flows through the radiator,
It passes through a series of thin, flat tubes that dissipate the heat and cool the coolant. The cooled coolant then flows back into the engine through the water pump, and the cycle begins again.
Throughout this process, the coolant lines connect the various components of the system, including the radiator, water pump, thermostat, engine block, and cylinder head. The expansion tank also plays a crucial role in the coolant flow,
As it stores excess coolant and releases it back into the system as needed. The heater core, meanwhile, diverts some of the heated coolant from the engine to heat the cabin of the vehicle.
Each component of the coolant system plays a vital role in the flow path of the coolant through the 5.9 Cummins engine. The water pump circulates the coolant through the system, while the radiator and thermostat help to regulate its temperature.
The engine block and cylinder head generate the heat, which is absorbed by the coolant, and the coolant lines connect everything together. The expansion tank stores excess coolant and the heater core diverts some of the heated coolants to warm the cabin.
By working together, these components ensure that the engine operates at optimal temperatures and remains in good health.
Troubleshooting Coolant Flow Issues
Coolant flow issues can lead to significant problems in the 5.9 Cummins engine, including overheating, poor performance, and even engine damage. Here are some common issues and symptoms to look out for:
Common issues:
- Clogs in the coolant lines or radiator
- Malfunctioning thermostat
- Worn or damaged water pump
- Leaks in the system
- Improper coolant levels
Symptoms:
- Engine overheating
- Poor performance and acceleration
- Strange noises or smells from the engine
- Low coolant levels or leaks
- Steam or smoke coming from the engine
If you suspect that you are experiencing coolant flow issues, it’s essential to diagnose and resolve the problem as soon as possible. Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot and fix the problem:
- Check the coolant levels: Ensure that the coolant level is at the recommended level and that there are no leaks in the system. If the coolant level is low, add more coolant and check for leaks.
- Check the water pump: If the water pump is not functioning correctly, it can cause a coolant flow issue. Check for leaks, damage, or wear and tear on the water pump, and replace it if necessary.
- Inspect the thermostat: The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant through the system. If it’s not functioning correctly, it can cause issues with the coolant flow. Check the thermostat for proper operation and replace it if necessary.
- Inspect the radiator: The radiator can become clogged or damaged over time, causing coolant flow issues. Inspect the radiator for any signs of damage or clogs and replace it if necessary.
- Check the coolant lines: The coolant lines can become clogged or damaged, which can impede the flow of coolant. Inspect the lines for any signs of wear and tear, damage, or clogs, and replace them if necessary.
By taking these steps to diagnose and resolve coolant flow issues, you can keep your 5.9 Cummins engine running smoothly and avoid significant problems down the road.
Maintenance and Upkeep of the Coolant System
Proper maintenance of the coolant system is essential to ensuring optimal engine performance and avoiding costly repairs. Here are some recommended maintenance tasks and tips for keeping your coolant system in top shape:
Recommended maintenance tasks and schedules:
- Check the coolant level regularly: Make sure that the coolant level is at the recommended level and that there are no leaks in the system. If the coolant level is low, add more coolant and check for leaks.
- Replace the coolant: Over time, the coolant in your system can become contaminated or degraded, leading to decreased performance. Replace the coolant at least every two years or as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspect the water pump: The water pump is a critical component of the coolant system, and regular inspection can help prevent problems down the road. Inspect the water pump for leaks, damage, or wear and tear regularly.
- Inspect the thermostat: The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant through the system and can become stuck or malfunction over time. Inspect the thermostat regularly for proper operation and replace it if necessary.
- Flush the system: Flushing the coolant system can help remove any debris or contaminants that may have accumulated over time, improving performance and extending the life of the system.
Tips for ensuring optimal coolant flow and engine performance:
- Use the recommended coolant: Different engines require different types of coolant, so make sure you’re using the recommended type for your 5.9 Cummins engine.
- Keep the system clean: Dirt, debris, and other contaminants can impede the flow of coolant, leading to decreased performance. Keep the engine bay and coolant system clean and free of debris.
- Replace damaged components: If you notice any damage to the coolant system components, such as leaks or cracks, replace them as soon as possible to avoid more significant problems down the road.
- Regularly inspect the system: Regular inspections of the coolant system can help identify and address issues before they become more significant problems.
By following these recommended maintenance tasks and tips, you can keep your 5.9 Cummins engine’s coolant system in top shape and avoid costly repairs.
Cummins Low Flow Cooling System Diagram
The Cummins low-flow cooling system is a common design used in many Cummins engines. This system is designed to optimize engine performance by maintaining a consistent engine temperature, even under heavy loads or extreme conditions.
Understanding the Diagram
The Cummins low-flow cooling system diagram is a visual representation of how the coolant flows through the engine. It shows the main components of the cooling system and how they work together to regulate engine temperature.
The diagram typically includes the following components:
- Radiator: The radiator is responsible for dissipating heat from the coolant as it passes through the system. The radiator is typically located at the front of the engine bay.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates the coolant through the system, ensuring that it flows through the engine and radiator.
- Thermostat: The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant through the system by opening and closing as needed to maintain a consistent engine temperature.
- Coolant Lines: The coolant lines connect the various components of the cooling system, ensuring that coolant flows smoothly throughout the engine.
- Expansion Tank: The expansion tank serves as a reservoir for the coolant, allowing for changes in pressure and volume as the engine heats up and cools down.
- Heater Core: The heater core is responsible for providing heat to the cabin of the vehicle. It works by using hot coolant from the engine to warm the air that is circulated through the HVAC system.
Benefits of the Low-Flow Cooling System
The Cummins low-flow cooling system provides several benefits over other cooling system designs, including:
- Improved engine performance: By maintaining a consistent engine temperature, the low-flow cooling system helps improve engine performance and efficiency, even under heavy loads or extreme conditions.
- Reduced maintenance costs: The low-flow cooling system is designed to be low maintenance, with fewer parts and a simple design that is less prone to failure or leaks.
- Increased durability: The low-flow cooling system is designed to be more durable than other cooling system designs, with fewer parts that are less prone to wear and tear over time.
By understanding the Cummins low-flow cooling system diagram and its components, you can better maintain and care for your Cummins engine, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
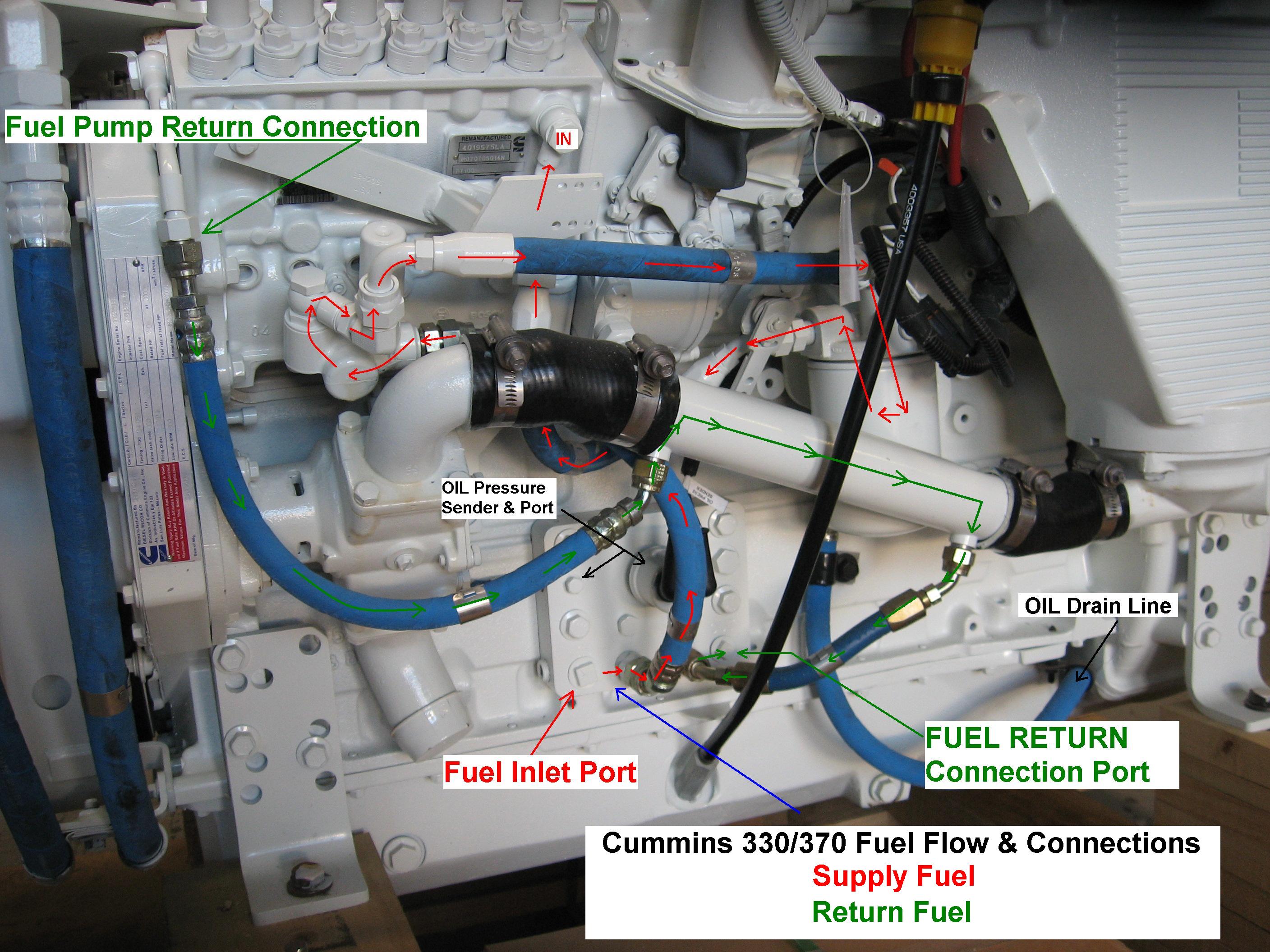
Credit: www.sbmar.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Cummins low-flow cooling system?
How does the low-flow cooling system work?
What are the benefits of the low flow cooling system?
What are some common issues with the low flow cooling system?
How can I maintain my Cummins low flow cooling system?
نظام التبريد للمحركات Coolant flow
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the coolant flow in the 5.9 Cummins engine is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing issues like overheating or engine failure.
By familiarizing yourself with the main components of the coolant system, troubleshooting common issues, and performing regular maintenance tasks, you can help ensure that your engine stays running smoothly for years to come.
Remember to check coolant levels and inspect for leaks or damage on a regular basis, as well as follow the recommended maintenance schedule outlined in your Cummins engine manual.
By taking these steps, you can help ensure that your engine operates efficiently and effectively, even under heavy loads or extreme conditions.
Read Also:







